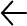Dominios cognitivos afectados en pacientes con depresión mayor
El compromiso de la función cognitiva es un componente central del trastorno depresivo mayor (TDM) y está asociado a:1-9
• Deterioro funcional significativo.
• Reducción importante del éxito del tratamiento psicoterapéutico.
• Disminución sustancial de la calidad de vida.
• Incremento del suicidio.
Hasta 70%-90% de los pacientes con trastorno depresivo mayor presentan deficien cias cognitivas.1,5
De todos los inhibidores selectivos de la recaptacion de la serotonina (ISRS) Fluvoxamina es Potente agonista de receptor sigma 1 lo que permite la mejoría de la función cognitiva.3,9,11-14
Referencias
- Hammar A, Ronold EH, Rekkedal GA. Cognitive impairment and neurocognitive profiles in major depression – a clinical perspective. Front Psychiatry 2022; 13: 764374.
- Zuckerman H, Pan Z, Park C, et al. Recognition and treatment of cognitive dysfunction in major depressive disorder. Front Psychiatry 2018; 9: 655-65.
- Bobrov A, Krasnoslobodtseva L, Mutnykh E. Effects of fluvoxamine on cognitive function in outpatients with depression in remission: results of an open-label pilot study. J Psychiatry 2017; 20: 5-10.
- Niitsu T, Iyo M, Hashimoto K. Sigma-1 receptor agonists as therapeutic drugs for cognitive impairment in neuropsychiatric diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 875-83.
- Liu J, Dong Q, Lu X, et al. Exploration of major cognitive deficits in medication-free patients with major depressive disorder. Front Psychiatry 2019; 10: 836-43.
- Kriesche D, Woll CFJ, Tschentscher N, et al. Neurocognitive deficits in depression: a systematic review of cognitive impairment in the acute and remitted state. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2023; 273: 1105-28.
- Culpepper L, Lam RW, McIntyre RS. Cognitive impairment in patients with depression: awareness, assessment, and management. J Clin Psychiatry 2017; 78: 1383-94.
- Woo YS, Rosenblat JD, Kakar R, et al. Cognitive deficits as a mediator of poor occupational function in remitted major depressive disorder patients. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 2016; 14: 1-16.
- Knight MJ, Lyrtzis E, Baune BT. The association of cognitive deficits with mental and physical quality of life in major depressive disorder. Compr Psychiatry 2020; 97: 152147.
- Ishikawa M, Ishiwata K, Ishii K, et al. High occupancy of sigma-1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of fluvoxamine: a positron emission tomography study using [11C]SA4503. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 62: 878-83.
- Hashimoto K. Sigma-1 receptors and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: clinical implications of their relationship. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 2009; 9:197-204.
- Albayrak Y, Hashimoto K. Sigma-1 receptor agonists and their clinical implications in neuropsychiatric disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017; 964: 153-61.
- Nishimura T, Ishima T, Iyo M, Hashimoto K. Potentiation of nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth by fluvoxamine: role of sigma-1 receptors, IP3 receptors and cellular signaling pathways. PLoS One 2008; 3: e2558.
- Härtter S, Wang X, Weigmann H, et al. Differential effects of fluvoxamine and other antidepressants on the biotransformation of melatonin. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2001; 21: 167-74.
- Von Bahar C, Ursing C, Yasui N, et al. Fluvoxamine but not citalopram increases serum melatonin in healthy subjects – an indication that cytochrome P450 CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 hydroxylate melatonin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2000; 56: 123-7.
- Sunami E, Usuda K, Nishiyama Y, et al. A preliminary study of fluvoxamine maleate on depressive state and serum melatonin levels in patients after cerebral infarction. Intern Med 2012; 51: 1187-93